A Deep Dive Into Sugar Cane: Insights on Production, Product, and Item Growth
Sugar cane plays a vital duty in farming, underpinning economies in exotic regions. Its farming entails detailed processes influenced by numerous environmental variables. Cultivators encounter significant obstacles, consisting of environment change and market changes. Developments in item development are arising in feedback to evolving customer demands. Recognizing these dynamics is vital for grasping the future of this essential crop and its effect on international markets. What lies ahead for sugar cane and its myriad applications?
The Importance of Sugar Cane in Global Agriculture
Sugar cane acts as a vital plant in worldwide farming, underpinning economic situations and food systems in many exotic areas. This functional plant is mainly grown for its high sucrose content, which is refined into sugar, an essential active ingredient in numerous food items. Past sweetening, sugar cane is likewise vital for producing biofuels, especially ethanol, adding to power sustainability.The economic importance of sugar cane reaches work, supplying livelihoods for millions of farmers and workers in processing facilities. In several countries, sugar cane cultivation and processing stand for considerable portions of farming GDP, affecting profession equilibriums and local development.Additionally, sugar cane's flexibility to numerous environments boosts its importance as a plant, making sure regular supply in worldwide markets. Its by-products, consisting of molasses and bagasse, even more expand its energy, making it a necessary part in food, energy, and industry. Overall, sugar cane continues to be a cornerstone of agricultural efficiency worldwide.
Growing Processes: From Growing to Harvest
Growing sugar cane involves a collection of distinct processes that ensure ideal growth and return. The cultivation begins with land prep work, where the soil is tilled to protect optimum aeration and drain. Following this, seed cane, which is composed of fully grown stalks, is chosen and reduced into sections (sugar cane products). These segments are after that planted in furrows, guaranteeing proper spacing to permit sunshine and nutrient access.Once planted, watering systems are employed to maintain ample moisture levels, as sugar cane grows in damp problems. Weeding and parasite administration are important during the expanding duration to lessen competition for resources. Nutrient application, consisting of fertilizers, sustains robust development. As the plants grow, monitoring for conditions and pests continues.Harvesting normally occurs 10 to 24 months post-planting, depending on the variety. The canes are reduced close to the ground, making certain marginal waste, and are promptly delivered for refining to maintain sugar top quality
Geographic Distribution of Sugar Cane Production
The geographic distribution of sugar cane production is mainly formed by details environment and dirt demands. Significant creating nations, such as Brazil, India, and China, gain from exotic and subtropical environments that support the plant's development. Recognizing these factors gives insight right into the worldwide landscape of sugar cane growing.
Major Making Countries
Sugar cane is expanded in different areas worldwide, particular nations dominate production due to favorable environments and agricultural practices - sugar cane products. Brazil leads the worldwide market, representing roughly one-third of complete production, thanks to its comprehensive haciendas and advanced growing methods. India follows as a considerable manufacturer, gaining from both positive climate condition and a large residential market. China and Thailand additionally rank amongst the leading producers, with reputable infrastructures sustaining their sugar markets. Other notable contributors include the United States, Mexico, and Australia, each leveraging their one-of-a-kind farming systems to enhance outcome. These countries play an essential duty in the sugar cane supply chain, affecting international rates and availability
Environment and Soil Needs
Suitable climate and soil conditions are important for successful sugar cane production. click Sugar cane flourishes in tropical and subtropical areas, requiring cozy temperatures between 20 ° C and 30 ° C (68 ° F to 86 ° F) These plants need abundant sunlight and rainfall, ideally between 1,500 to 2,500 millimeters every year, to assure peak growth. The dirt needs to be well-drained, fertile, and abundant in raw material, with a pH level ideally between 5.5 and 8.5. Sandy loam or clay loam dirts are especially for sugar cane cultivation, giving essential nutrients and drain. Geographic distribution is greatly influenced by these elements, with major production areas located in Brazil, India, and China, where ecological problems align with the plant's requirements for development and return.

Obstacles Encountered by Sugar Cane Growers
Sugar cane farmers come across substantial obstacles that impact their livelihoods. Environment modification introduces unforeseeable climate patterns, influencing plant yield and high quality. In addition, market value volatility creates financial unpredictability, complicating long-lasting preparation for these agricultural producers.
Climate Modification Impacts

Exactly how do environment adjustment impacts influence the practicality of sugar cane cultivation? their explanation Increasing temperatures and irregular weather patterns notably test sugar cane farmers. Increased warm can cause decreased yields, as the plants battle to flourish in severe conditions. Additionally, transformed rainfall patterns lead to either droughts or extreme flooding, both harmful to plant health. Insects and illness are likely to proliferate in warmer climates, further harmful production. Dirt degradation and salinization due to climbing sea degrees can decrease arable land. These weather adjustments compel farmers to adjust their practices, often calling for financial investment in brand-new modern technologies and resistant crop ranges. Ultimately, the sustainability of sugar cane growing rests on addressing these environment challenges efficiently.
Market Value Volatility
Market price volatility provides substantial obstacles for sugar cane farmers, influencing their financial stability and planning. Fluctuations in market rates, driven by aspects such as international supply and need, climate condition, and federal government policies, develop unpredictability for producers. This changability makes it tough for farmers to forecast earnings and manage operating budget properly. In addition, when rates drop unexpectedly, numerous farmers may have a hard time to cover production costs, causing prospective monetary distress. To reduce these threats, some cultivators transform to agreements or hedging methods, yet these solutions might not come to all. Market rate volatility continues to be a relentless concern, affecting the general sustainability and success of sugar cane farming.
Understanding the Sugar Cane Supply Chain

Market Patterns Affecting Sugar Cane Prices
The characteristics of sugar cane costs are affected by a range of market patterns that mirror broader economic conditions and customer behaviors. Worldwide demand for sugar and sugar-related items plays an essential duty, with boosting rate of interest in organic and sustainably sourced products driving costs higher. Furthermore, changes in oil rates impact the cost of production and transportation, additional affecting market rates. Weather patterns are one more considerable element; adverse problems can cause decreased yields and boosted costs. Profession policies, tariffs, and international agreements likewise form the marketplace landscape, influencing supply chains and availability. Currency exchange prices can complicate international profession, affecting rates for both exporters and importers. Finally, shifts in consumer choices toward healthier options may modify demand patterns, developing a causal sequence on sugar cane prices. Recognizing these interconnected patterns is vital for stakeholders in the sugar sector.
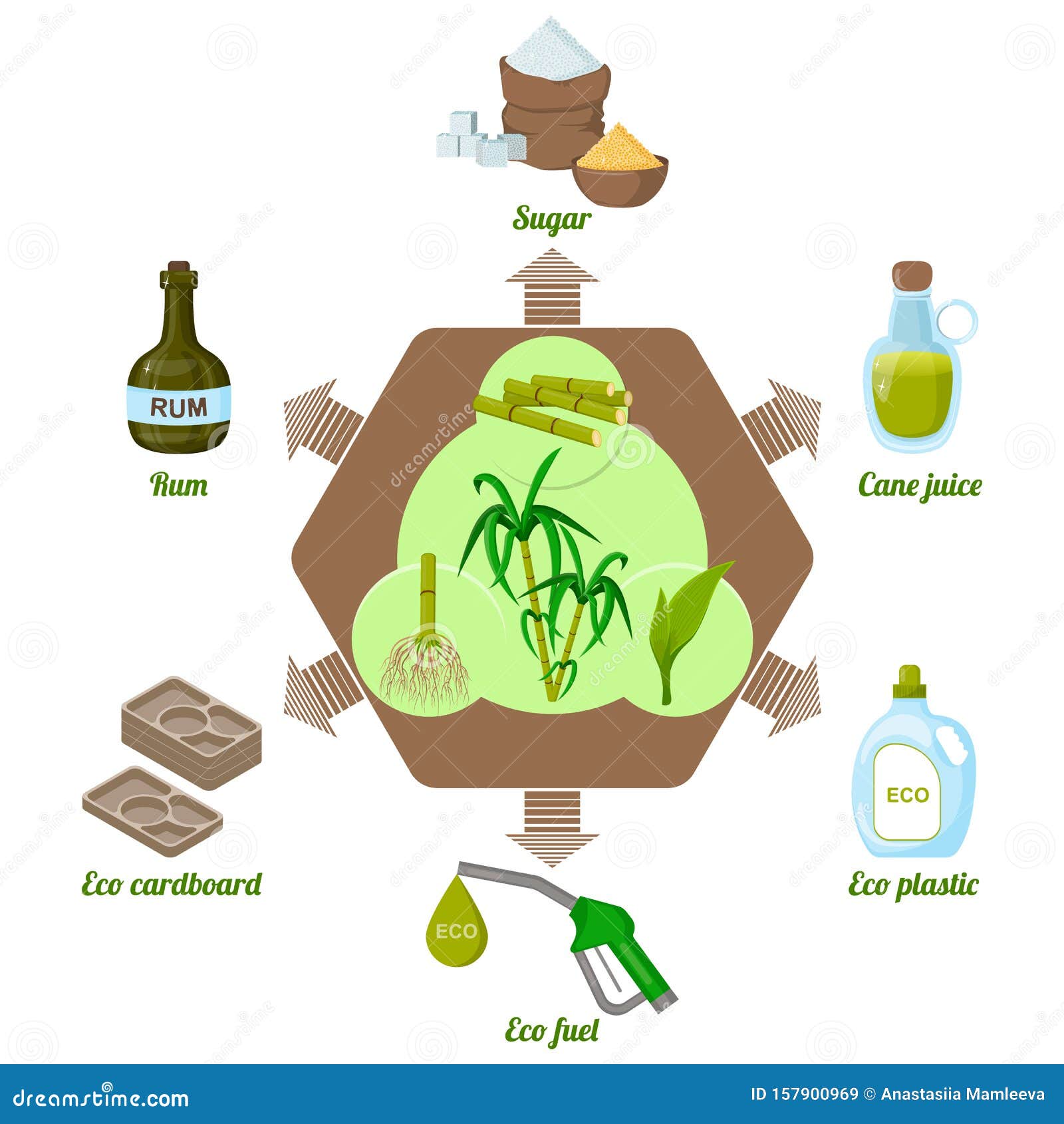
Developments in Sugar Cane Product Growth
Numerous advancements in sugar cane product growth are improving the industry and expanding its applications. Researchers are exploring alternative uses beyond standard sugar, consisting of biofuels, eco-friendly plastics, and wellness supplements. Advances in enzymatic handling methods have actually enhanced the extraction of beneficial compounds such as antioxidants and vitamins from sugar cane, promoting its use in useful foods.Additionally, the growth of genetically changed sugar cane ranges aims to boost return and resistance to bugs, while additionally improving the dietary profile of the crop. Innovations in fermentation procedures have actually caused the production of premium alcohols originated from sugar cane, appealing to an expanding market for craft spirits.Moreover, sustainable practices in cultivation and processing are gaining grip, with a concentrate on minimizing environmental influences. These advancements their explanation not only create new market chances yet additionally cultivate a more lasting technique to sugar cane production, aligning with worldwide fads towards eco-friendly products.
Regularly Asked Inquiries
What Are the Ecological Effects of Sugar Cane Farming?
The environmental effects of sugar cane farming consist of deforestation, loss of biodiversity, water contamination from fertilizers and pesticides, soil deterioration, and greenhouse gas exhausts, every one of which considerably add to ecological discrepancies and environment modification.
How Does Sugar Cane Farming Affect Local Economies?
Sugar cane growing greatly affects regional economies by creating tasks, promoting farming markets, and creating income for farmers. Nonetheless, it can likewise lead to economic reliance and fluctuations based on market needs and ecological conditions.
What Are the Key Pests and Diseases Affecting Sugar Cane?
The primary bugs influencing sugar cane consist of the sugarcane borer and aphids. Conditions such as red rot and smut substantially impact return. Farmers should apply integrated pest administration strategies to minimize these dangers efficiently.
Just How Is Sugar Cane Processed Into Different Products?
Sugar cane handling involves squashing the stalks to draw out juice, adhered to by explanation, evaporation, and condensation. This process returns raw sugar, molasses, and ethanol, each offering distinct purposes in different industries, from food to power.
What Are the Nutritional Aspects of Sugar Cane?
The nutritional elements of sugar cane consist of necessary minerals and vitamins, specifically B vitamins, calcium, and iron. It additionally contains fiber, though largely made up of sucrose, which gives energy but does not have substantial nutrients.